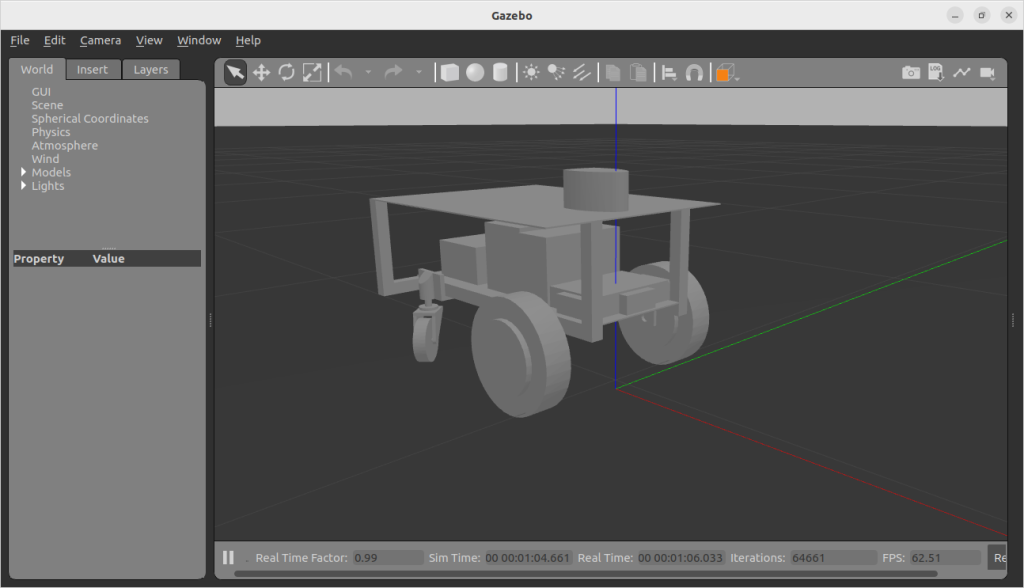
3次元CADのSOLIDWORKSを使って自律移動ロボットを設計します。
3Dデータを使用して、ROSで表示するためにモデリングします。
ROSの表示ツールRViz2で自律移動ロボットを表示して確かめます。
シミュレータGazebo上でシミュレーションするために、Gazeboのプラグインを追加します。
シミュレータ上で自律移動ロボットの動作を確かめます。
自律移動ロボット(AMR)を3D CADで設計
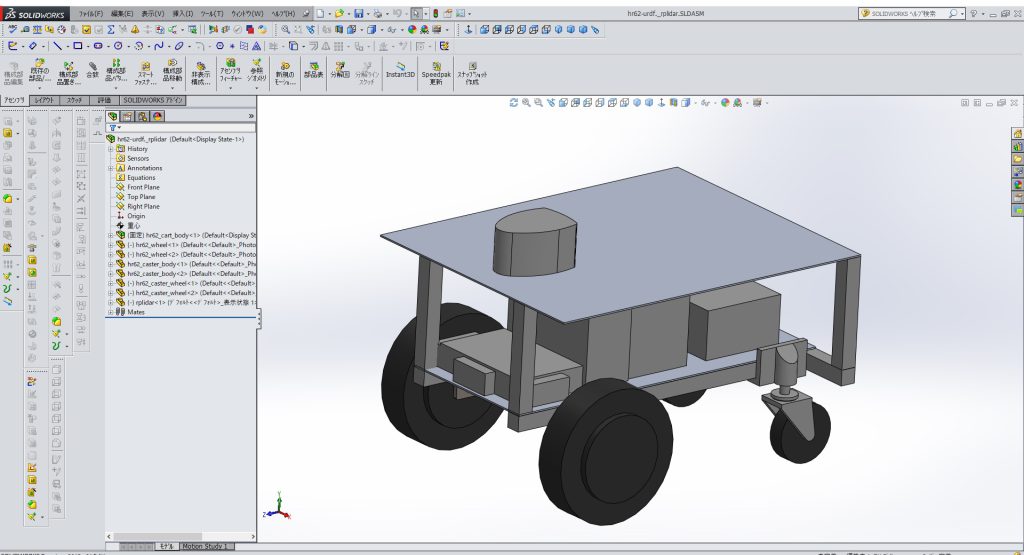
3D CADで自律移動ロボット(AMR)を設計します。以下の例では、3D CADは、SOLIDWORKSを使用しています。
部品の3DデータをSTL形式で出力します。また、CADで計算された重量、慣性モーメントの値も記録します。
3DCADで自律移動ロボットのデザイン
ROSで表示やシミュレーションに使う場合は、機械設計で使用した詳細な3Dモデルとは別の簡素化した3Dモデルを用います。ファイルサイズの縮小とシミュレーション時間短縮になります。
(下図の赤字は説明のために追記したものです。)
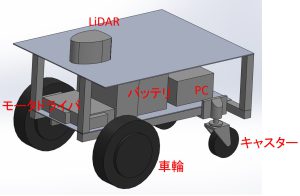
メカニズムをシンプルにするために、ステアリング機構は使わず、差動駆動の台車で、自律移動ロボットを設計しました。
前輪の二輪が独立して駆動する仕組みです。後輪の二輪は、自在キャスターで、360度回転し色々な方向に向くことができます。
前輪の左右の車輪の回転速度を変えると、台車が左右に旋回しながら進んだり、その場で回転することができます。真横には移動できません。
例えば、右車輪を前進方向に回し、左車輪を後退方向に同じ速さで回すと、台車はその場で左回転します。このときの回転中心は、左右車輪の中心になります。自律移動ロボットの座標軸の原点はこの回転軸上にとる必要があります(下の画像の水色の座標軸(小さいです))。
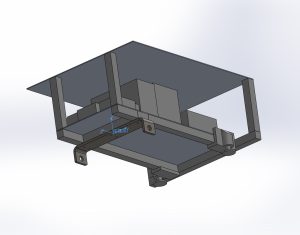
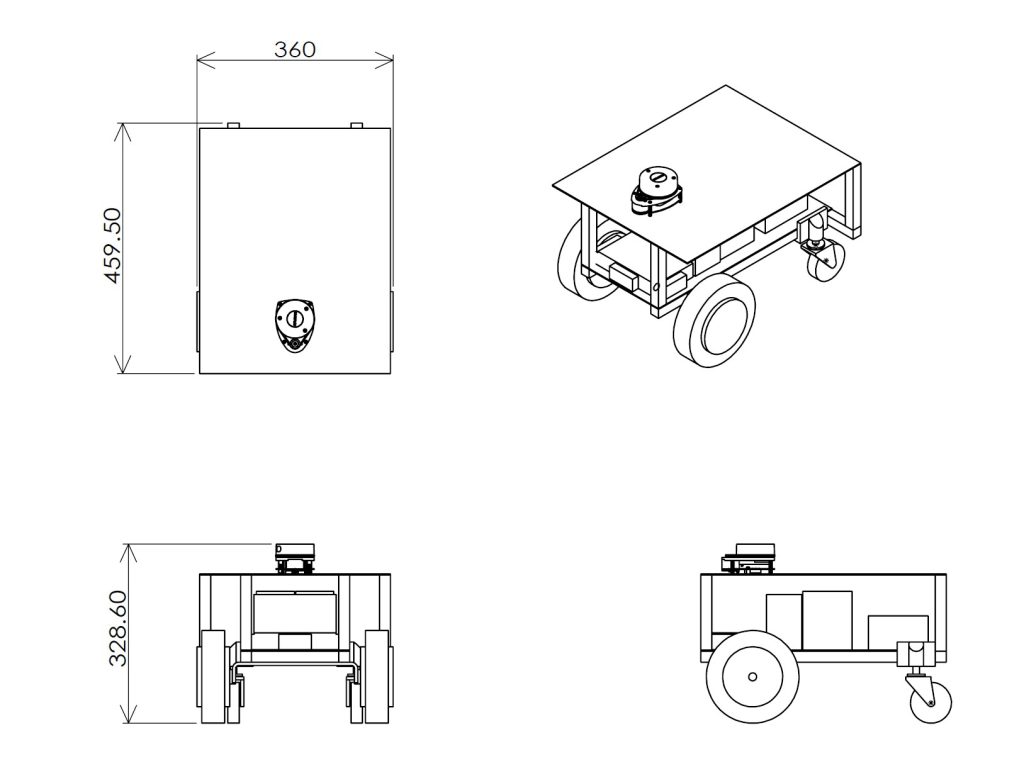
自律移動ロボットの図面
部品形状をSTL形式で出力
ROS上でロボットをモデリングするために、3D CADから、3Dのパーツやアセンブリの形状をSTL形式で出力します。
ROSのシミュレーション(Gazebo)に使うモデルには簡素化したデータを使います。機械設計に用いる詳細なデータそのままだとシミュレーションが遅くなります。
今回のように自律移動ロボットのナビゲーションに使うだけなら、見栄えにこだわらなければ、STLファイルでなくても、直方体や円柱の組み合わせでも問題ないと思います。その方がシミュレーションが早くなります。
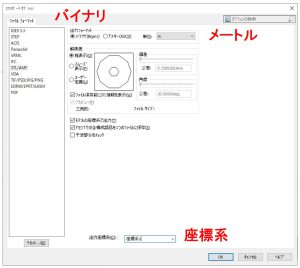
STLの出力フォーマットはバイナリ、単位はメートル、座標軸は組み立てやすい位置に設定します。(下図の赤字は説明のために追記したものです。)STLは粗くて問題ありません。関節位置などの基準になる点を座標軸の原点にとると、ROSのURDFファイルで記述しやすくなります。
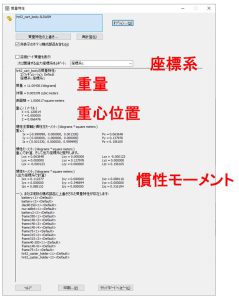
シミュレーションをより現実に近づけたいときは、重量、重心位置、慣性モーメントを、CADから取得します。このとき、基準の座標系を確認し、単位はROS(メートル、キログラム)に合わせるのを忘れないようにします。(下図の赤字は説明のために追記したものです。)
ROSの環境で自律移動ロボット(AMR)を表示できるようにモデリング
ROSではロボットをURDFのファイル形式で表現します。
3D CADで作成したSTLファイルを使って、自律移動ロボット(AMR)のURDFのファイルを作成します。
ROS2の表示ツール「RViz2」で自律移動ロボットを表示して、URDFが正しいことを確認します。
以下は、ROS2の humble を使用した例です。
自律移動ロボットのモデルファイル(URDF)の作成
画面表示用のvisual要素には、パーツのSTLファイルを指定します。
干渉用(衝突計算用)のcollision要素には、STLファイルを使わず直方体や円柱の要素を用いても構いません。
シミュレータ用のinertia要素の、重量や慣性モーメントには、CADで計算された値を用います。
joint要素を使用して、 link要素とlink要素を結合して組み立てていき、自律移動ロボットのURDFファイルを完成させます。
hajimecart.urdf
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<robot name="hajimecart">
<link name="base_footprint"/>
<link name="base_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/hr62_cart_body.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/hr62_cart_body_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="11.0044"/>
<origin xyz="-0.120614 0 0.066476" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.112277" iyy="0.346694" izz="0.316194" ixy="0.000" ixz="-0.08811" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="base_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="0 0 0.112" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="base_footprint"/>
<child link="base_link" />
</joint>
<link name="right_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/wheel.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/wheel_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="2.9"/>
<origin xyz="0 -0.034923 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.008958" iyy="0.009528" izz="0.008958" ixy="0.000" ixz="0.000" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="right_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0.000 -0.115 -0.027" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="right_wheel_link"/>
</joint>
<link name="left_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/wheel.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="3.141592654 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/wheel_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="3.141592654 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="2.9"/>
<origin xyz="0 0.034923 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.008958" iyy="0.009528" izz="0.008958" ixy="0.000" ixz="0.000" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="left_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="0.000 0.115 -0.027" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_wheel_link"/>
</joint>
<link name="right_caster_body_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_body.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_body_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.260"/>
<origin xyz="-0.010065 0 -0.017514" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.000191" iyy="0.000211" izz="0.000125" ixy="0.000" ixz="0.000074" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="right_caster_body_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="-0.300 -0.113 -0.0256" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 0 1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="right_caster_body_link"/>
</joint>
<link name="left_caster_body_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_body.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_body_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.260"/>
<origin xyz="-0.010065 0 -0.017514" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.000191" iyy="0.000211" izz="0.000125" ixy="0.000" ixz="0.000074" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="left_caster_body_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="-0.300 0.113 -0.0256" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 0 1"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="left_caster_body_link"/>
</joint>
<link name="right_caster_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_wheel.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_wheel.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.050"/>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.000019" iyy="0.000035" izz="0.000019" ixy="0.000" ixz="0.000" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="right_caster_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="-0.027 0 -0.0489" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
<parent link="right_caster_body_link"/>
<child link="right_caster_wheel_link"/>
</joint>
<link name="left_caster_wheel_link">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_wheel.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/caster_wheel.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.050"/>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.000019" iyy="0.000035" izz="0.000019" ixy="0.000" ixz="0.000" iyz="0.000"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="left_caster_wheel_joint" type="continuous">
<origin xyz="-0.027 0 -0.0489" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<axis xyz="0 1 0"/>
<parent link="left_caster_body_link"/>
<child link="left_caster_wheel_link"/>
</joint>
<link name="base_scan">
<visual>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/rplidar_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<material name="white">
<color rgba="1 1 1 1"/>
</material>
</visual>
<collision>
<geometry>
<mesh filename="file://$(find hajimecart_description)/meshes/rplidar_col.stl" />
</geometry>
<origin xyz="0 0 0" rpy="0 0 0"/>
</collision>
<inertial>
<mass value="0.218"/>
<origin xyz="0.011760 -0.000741 -0.020473" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<inertia ixx="0.000184" iyy="0.000296" izz="0.000234" ixy="-1.0e-6" ixz="-6.9e-5" iyz="1.0e-6"/>
</inertial>
</link>
<joint name="scan_joint" type="fixed">
<origin xyz="-0.005 0 0.2076" rpy="0 0 0"/>
<parent link="base_link"/>
<child link="base_scan"/>
</joint>
</robot>
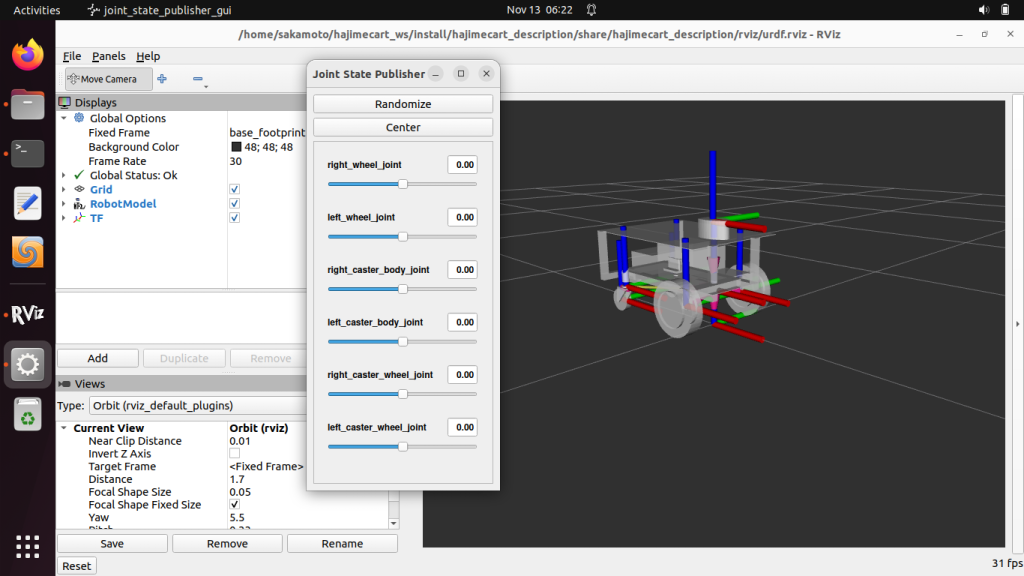
自律移動ロボットの表示(URDFファイルの確認)
ROS2の表示ツール「RViz2」で自律移動ロボットを表示して、URDFが正しいことを確認します。
ros2 launch hajimecart_description display.launch.py gui:=true
display.launch.py
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_path
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.conditions import IfCondition, UnlessCondition
from launch.substitutions import Command, LaunchConfiguration
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch_ros.parameter_descriptions import ParameterValue
def generate_launch_description():
use_sim_time = LaunchConfiguration('use_sim_time', default='True')
urdf_model_dir = get_package_share_path('hajimecart_description')
urdf_model_path = os.path.join(urdf_model_dir, 'urdf', 'hajimecart.urdf')
rviz_config_dir = get_package_share_path('hajimecart_description')
rviz_config_path = os.path.join(rviz_config_dir, 'rviz', 'urdf.rviz')
gui_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(name='gui', default_value='false', choices=['true', 'false'],
description='Flag to enable joint_state_publisher_gui')
model_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(name='model', default_value=str(urdf_model_path),
description='Absolute path to robot urdf file')
rviz_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(name='rvizconfig', default_value=str(rviz_config_path),
description='Absolute path to rviz config file')
robot_description = ParameterValue(Command(['xacro ', LaunchConfiguration('model')]),
value_type=str)
robot_state_publisher_node = Node(
package='robot_state_publisher',
executable='robot_state_publisher',
parameters=[{'use_sim_time': use_sim_time, 'robot_description': robot_description}]
)
# Depending on gui parameter, either launch joint_state_publisher or joint_state_publisher_gui
joint_state_publisher_node = Node(
package='joint_state_publisher',
executable='joint_state_publisher',
condition=UnlessCondition(LaunchConfiguration('gui'))
)
joint_state_publisher_gui_node = Node(
package='joint_state_publisher_gui',
executable='joint_state_publisher_gui',
condition=IfCondition(LaunchConfiguration('gui'))
)
rviz_node = Node(
package='rviz2',
executable='rviz2',
name='rviz2',
output='screen',
arguments=['-d', LaunchConfiguration('rvizconfig')],
)
return LaunchDescription([
gui_arg,
model_arg,
rviz_arg,
joint_state_publisher_node,
joint_state_publisher_gui_node,
robot_state_publisher_node,
rviz_node
])
<補足>STLファイルの中身にsolidの文字があれば警告が出ることがあります。その場合、先頭にあるsolidの文字を、例えばsssssに置換しておきます。(私のSOLIDWORKSではこうした方がよい)
sed -i 's/^solid/sssss/' *.stl
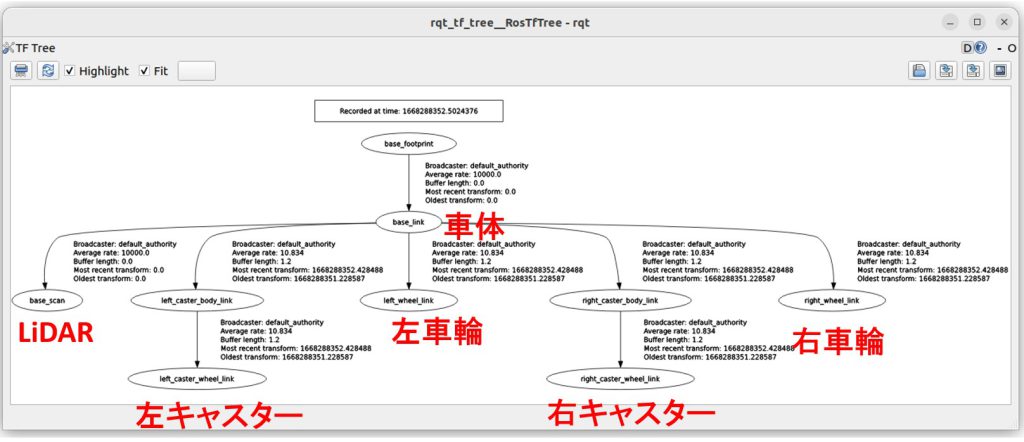
自律移動ロボットの座標系の確認
rqt_tf_treeで自律移動ロボットの各リンクの座標系の関係を表示します。
ros2 run rqt_tf_tree rqt_tf_tree
sudo apt install ros-humble-rqt-tf-tree
シミュレーション用の自律移動ロボット(AMR)を作成
ROS2のシミュレータとして、「Gazebo」を使います。
自律移動ロボットのURDFのファイルに、シミュレーションに必要なGazebo用の要素を追加します。
ROS2のシミュレータ「Gazebo」で自律移動ロボットをシミュレーションして、キーボードとジョイパッドから、自律移動ロボットが操縦できることを確認します。
シミュレーション用のURDFファイルを準備
プラグインの追加により自律移動ロボット実機の代わりをさせます。
hajimecart_gazebo.urdf(抜粋)
<gazebo>
<plugin name="differential_drive_controller" filename="libgazebo_ros_diff_drive.so">
<ros>
<argument>cmd_vel:=cmd_vel</argument>
<argument>odom:=odom</argument>
</ros>
<update_rate>20</update_rate>
<left_joint>left_wheel_joint</left_joint>
<right_joint>right_wheel_joint</right_joint>
<wheel_separation>0.300</wheel_separation>
<wheel_diameter>0.170</wheel_diameter>
<odometry_frame>odom</odometry_frame>
<max_wheel_torque>10</max_wheel_torque>
<max_wheel_acceleration>1</max_wheel_acceleration>
<publish_odom>true</publish_odom>
<publish_odom_tf>true</publish_odom_tf>
<publish_wheel_tf>false</publish_wheel_tf>
<robot_base_frame>base_footprint</robot_base_frame>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
<gazebo>
<plugin name="joint_states" filename="libgazebo_ros_joint_state_publisher.so">
<ros>
<remapping>~/out:=joint_states</remapping>
</ros>
<update_rate>20</update_rate>
<joint_name>right_wheel_joint</joint_name>
<joint_name>left_wheel_joint</joint_name>
<joint_name>right_caster_body_joint</joint_name>
<joint_name>left_caster_body_joint</joint_name>
<joint_name>right_caster_wheel_joint</joint_name>
<joint_name>left_caster_wheel_joint</joint_name>
</plugin>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="base_scan">
<sensor type="ray" name="rplidar">
<pose>0 0 0 0 0 0</pose>
<ray>
<scan>
<horizontal>
<samples>360</samples>
<resolution>1</resolution>
<min_angle>-3.14159265</min_angle>
<max_angle>3.14159265</max_angle>
</horizontal>
</scan>
<range>
<min>0.15</min>
<max>12.0</max>
<resolution>0.12</resolution>
</range>
<noise>
<type>gaussian</type>
<mean>0.0</mean>
<stddev>0.01</stddev>
</noise>
</ray>
<always_on>true</always_on>
<visualize>false</visualize>
<update_rate>5</update_rate>
<plugin name="laser" filename="libgazebo_ros_ray_sensor.so">
<ros>
<remapping>~/out:=scan</remapping>
</ros>
<output_type>sensor_msgs/LaserScan</output_type>
<frame_name>base_scan</frame_name>
</plugin>
</sensor>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="right_wheel_link">
<mu1>1.0</mu1>
<mu2>1.0</mu2>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="left_wheel_link">
<mu1>1.0</mu1>
<mu2>1.0</mu2>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="right_caster_wheel_link">
<mu1>0.1</mu1>
<mu2>0.1</mu2>
</gazebo>
<gazebo reference="left_caster_wheel_link">
<mu1>0.1</mu1>
<mu2>0.1</mu2>
</gazebo>
シミュレータ(Gazebo)の起動
Gazeboを起動して、自律移動ロボットを配置します。
ros2 launch hajimecart_gazebo empty_world.launch.py
empty_world.launch.py
import os
from ament_index_python.packages import get_package_share_directory
from launch import LaunchDescription
from launch.actions import DeclareLaunchArgument
from launch.actions import IncludeLaunchDescription
from launch.launch_description_sources import PythonLaunchDescriptionSource
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch_ros.parameter_descriptions import ParameterValue
from launch.substitutions import Command, LaunchConfiguration
def generate_launch_description():
pkg_gazebo_ros = get_package_share_directory('gazebo_ros')
pkg_my_gazebo = get_package_share_directory('hajimecart_gazebo')
worlds = os.path.join(pkg_my_gazebo, 'worlds', 'empty_worlds.world')
urdf_model_dir = get_package_share_directory('hajimecart_description')
urdf_model_path = os.path.join(urdf_model_dir, 'urdf', 'hajimecart_gazebo.urdf')
model_arg = DeclareLaunchArgument(name='model', default_value=str(urdf_model_path),
description='Absolute path to robot urdf file')
robot_description = ParameterValue(Command(['xacro ', LaunchConfiguration('model')]),
value_type=str)
# Gazebo launch
gazebo = IncludeLaunchDescription(
PythonLaunchDescriptionSource(
os.path.join(pkg_gazebo_ros, 'launch', 'gazebo.launch.py'),
)
)
spawn_entity = Node(package='gazebo_ros', executable='spawn_entity.py',
arguments=['-entity', 'hajimecart', '-topic', '/robot_description'],
output='screen')
robot_state_publisher = Node(
package='robot_state_publisher',
executable='robot_state_publisher',
parameters=[{'robot_description': robot_description}]
)
return LaunchDescription([
DeclareLaunchArgument(
'world',
default_value=[worlds, ''],
description='SDF world file'),
model_arg,
gazebo,
spawn_entity,
robot_state_publisher
])
empty_worlds.model
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<sdf version="1.6">
<world name="default">
<include>
<uri>model://sun</uri>
</include>
<include>
<uri>model://ground_plane</uri>
</include>
</world>
</sdf>
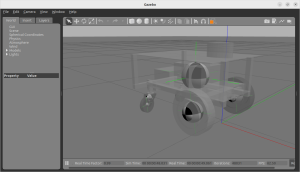
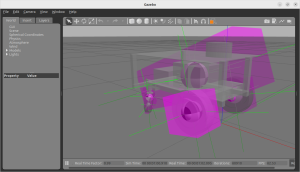
重心を表示して、URDFファイルの記述に間違いがないことを視覚的に確かめます。重心マークの球の位置と大きさを見ます。質量が大きいと、球も大きくなります。
キーボードで自律移動ロボットを操縦
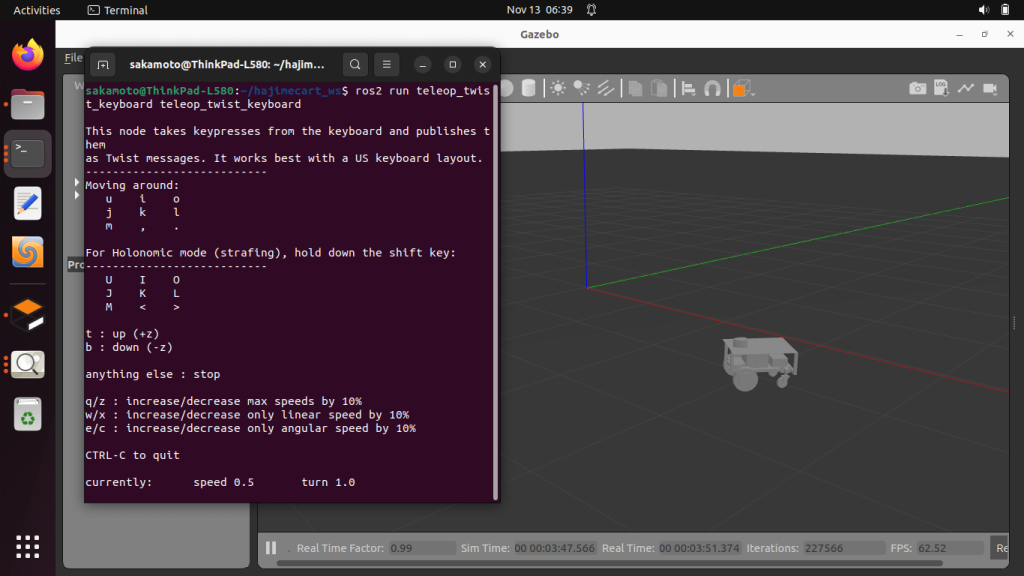
Gazeboに配置されている自律移動ロボットは動かせます。
キーボードで自律移動ロボットを操縦する場合は、キーボードのキーを速度指令に変換するプログラムを起動します。
ros2 run teleop_twist_keyboard teleop_twist_keyboard
このプログラムがなければ、インストールします。
sudo apt install ros-humble-teleop-twist-keyboard
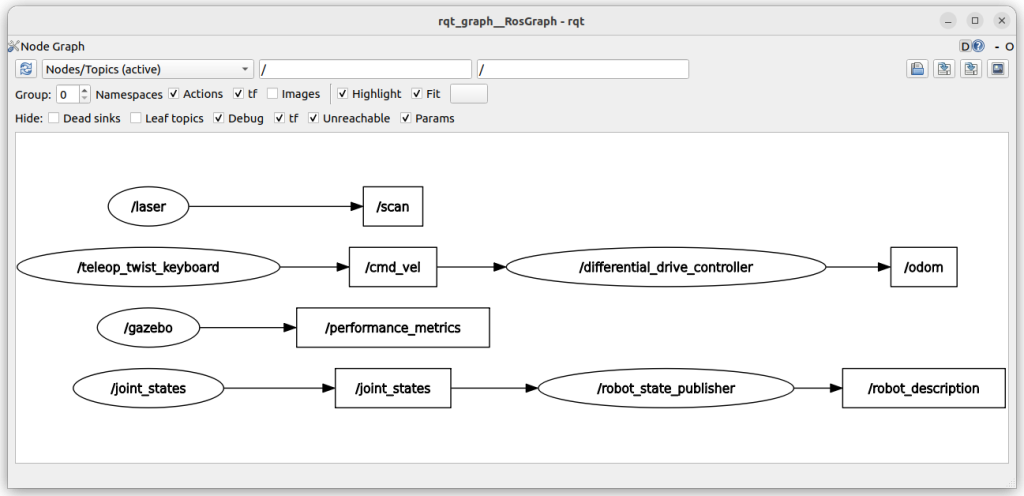
ros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph
キーボードのキーを速度指令に変換するプログラム(teleop_twist_keyboard)が、キーボードのキーを速度指令(/cmd_vel)に変換しています。それが、Gazeboのプラグイン(differencial_drive_controller)につながっています。
ROSでは、ノード(プログラム)(rqt_graphのの表示では楕円)は、メッセージ(rqt_graphのの表示では四角形)を介してつながります。下図でもそのようになっています。
ジョイパッド(ゲーム用コントローラ)で自律移動ロボットを操縦
ジョイパッドは、PCゲーム用のコントローラです。
Gazeboを起動して、自律移動ロボットを配置します。
ros2 launch hajimecart_gazebo empty_world.launch.py
ジョイパッドを使って、Gazeboに配置されている自律移動ロボットを操縦します。
ジョイパッドのデータを読み込むプログラムを起動します。
ros2 run joy_linux joy_linux_node _dev:=/dev/input/js0
ジョイパッドのデータ(joy)を自律移動ロボットの速度指令(/cmd_vel)に変換するプログラム(teleop_joy.cpp)を作成します。
teleop_joy.cpp
#include "rclcpp/rclcpp.hpp"
#include "geometry_msgs/msg/twist.hpp"
#include "sensor_msgs/msg/joy.hpp"
using namespace std::chrono_literals;
class TeleopJoy : public rclcpp::Node
{
public:
TeleopJoy()
: Node("teleop_joy")
{
RCLCPP_INFO(this->get_logger(), "TeleopJoy");
auto default_qos = rclcpp::QoS(rclcpp::SystemDefaultsQoS());
subscription_ = this->create_subscription(
"joy", default_qos, std::bind(&TeleopJoy::subscription_callback, this, std::placeholders::_1));
publisher_ = this->create_publisher("cmd_vel", default_qos);
timer_ = this->create_wall_timer(
10ms, std::bind(&TeleopJoy::timer_callback, this)); // 100Hz(10ms)
}
private:
void subscription_callback(const sensor_msgs::msg::Joy::SharedPtr msg)
{
cmd_vel_linear_x_ = msg->axes[1] * max_vel_x_;
cmd_vel_angular_z_ = msg->axes[0] * max_vel_th_;
}
void timer_callback()
{
geometry_msgs::msg::Twist cmd_vel;
cmd_vel.linear.x = cmd_vel_linear_x_;
cmd_vel.linear.y = 0.0;
cmd_vel.linear.z = 0.0;
cmd_vel.angular.x = 0.0;
cmd_vel.angular.y = 0.0;
cmd_vel.angular.z = cmd_vel_angular_z_;
publisher_->publish(cmd_vel);
}
rclcpp::Subscription::SharedPtr subscription_;
rclcpp::TimerBase::SharedPtr timer_;
rclcpp::Publisher::SharedPtr publisher_;
double cmd_vel_linear_x_ = 0.0;
double cmd_vel_angular_z_ = 0.0;
double max_vel_x_ = 1.0;
double max_vel_th_ = 3.141592654;
};
int main(int argc, char * argv[])
{
rclcpp::init(argc, argv);
rclcpp::spin(std::make_shared());
rclcpp::shutdown();
return 0;
}
これを起動します。
ros2 run teleop_joy teleop_joy
Launchファイルでこれらをまとめて起動することもできます。
ros2 launch teleop_joy teleop_joy.launch.py
teleop_joy.launch.py
from launch_ros.actions import Node
from launch import LaunchDescription
def generate_launch_description():
teleop_joy = Node(
package='teleop_joy',
executable='teleop_joy',
name='teleop_joy',
output='screen',
)
joy_linux = Node(
package='joy_linux',
executable='joy_linux_node',
name='joy_linux',
output='screen',
remappings=[('_dev', '/dev/input/js0')]
)
return LaunchDescription([
teleop_joy,
joy_linux
])
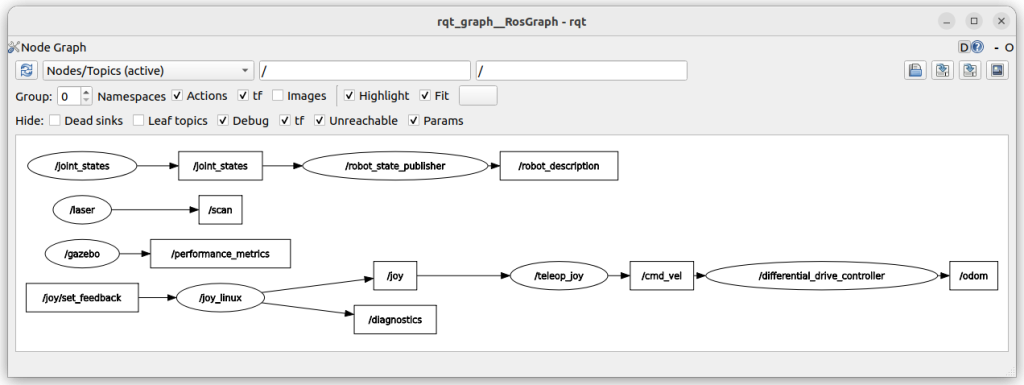
ros2 run rqt_graph rqt_graph
作成したプログラム(teleop_joy)で、joy_linuxのデータ(/joy)を、速度指令(/cmd_vel)に変換しています。それが、Gazeboのプラグイン(differencial_drive_controller)につながっています。